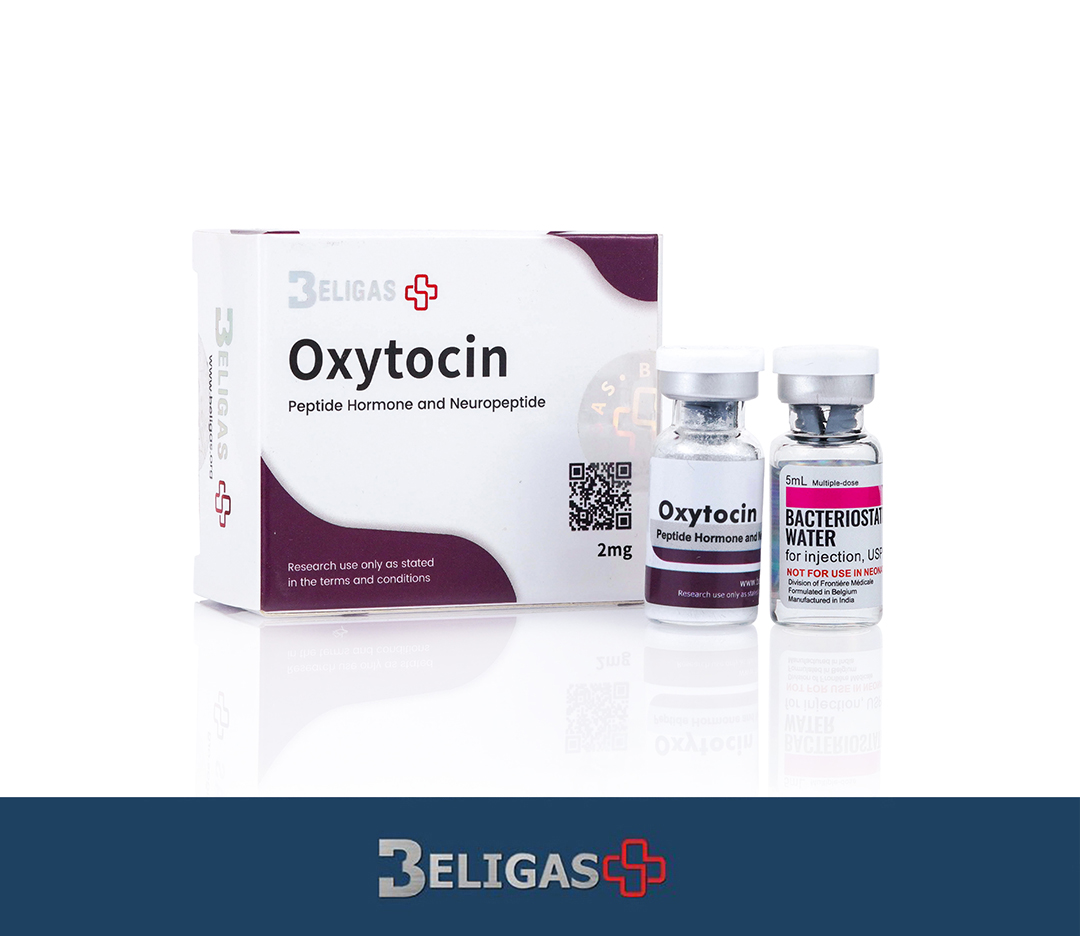
Oxytocin 2mg
$33.00 Original price was: $33.00.$24.00Current price is: $24.00.
PROFILE
- Raw: Oxytocin
- Chemical Name: Oxytocin
- Effective Dose (men): 10-20 IU (International Units) per injection (depending on goals and individual response)
- Effective Dose (women): 10-20 IU per injection (depending on goals and individual response)
- Active Life: 20-30 minutes (effects typically last for a short period of time)
- Detection Time: Not well documented (likely short, as it is a natural hormone)
- Anabolic/Androgenic Ratio: Not applicable (Oxytocin is a peptide hormone, not an anabolic steroid)
- Formulation: Powder form (2mg per vial), reconstituted with Bacteriostatic Water
Key Information about Oxytocin (2mg):
Primary Use:
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone produced in the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes, such as childbirth and lactation. In recent years, Oxytocin has gained popularity for its potential use in promoting bonding, social interactions, mood enhancement, and stress reduction. It is often referred to as the “love hormone” or the “bonding hormone” because of its role in emotional bonding, trust, and affection. Oxytocin is also used in medical settings for inducing labor, enhancing uterine contractions, and facilitating milk ejection during breastfeeding.
In addition to its traditional medical uses, Oxytocin has been explored for its potential benefits in improving mental health, emotional well-being, and muscle recovery.
Mechanism of Action:
Oxytocin works by binding to specific oxytocin receptors found throughout the body, particularly in the uterus, breasts, and brain. In the brain, Oxytocin influences regions responsible for social behavior, emotional regulation, and trust. It has been shown to increase feelings of bonding, empathy, and positive social interactions.
- In Childbirth: Oxytocin stimulates the uterus to contract during labor, and it also plays a key role in the delivery of the placenta.
- In Lactation: Oxytocin facilitates milk ejection from the breast during breastfeeding by causing contraction of the mammary glands.
- Social Bonding: Oxytocin helps promote pair bonding, maternal bonding, and can enhance feelings of love, trust, and connection. It is thought to increase empathy, generosity, and prosocial behavior.
- Stress Reduction: Oxytocin has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, as it helps regulate the body’s fight or flight response and promotes feelings of calmness.
Common Uses:
- Childbirth and Labor Induction: Oxytocin is widely used in clinical settings to induce labor in pregnant women or to strengthen uterine contractions during childbirth.
- Postpartum Hemorrhage: Oxytocin is also used to help prevent excessive bleeding after childbirth by promoting uterine contractions to close blood vessels.
- Milk Ejection: In lactating women, Oxytocin facilitates the release of milk by stimulating the mammary glands.
- Emotional and Social Bonding: Oxytocin is commonly used in research or non-medical contexts to improve emotional well-being and strengthen social bonds between individuals. It is often used by those interested in improving relationships, trust, or emotional intimacy.
- Mental Health: Oxytocin has been studied for its potential to reduce stress, anxiety, and symptoms of depression. It may promote positive feelings and improve mood, particularly in individuals who experience high levels of social stress or isolation.
- Muscle Recovery and Performance: There is ongoing research into the use of Oxytocin in athletes and bodybuilders to promote muscle recovery and reduce inflammation. Its potential benefits for muscle repair come from its role in tissue regeneration and enhancing overall healing after exercise-induced stress.
Dosing Guidelines:
- Men (Social Behavior, Emotional Health, and Recovery):
- Typical Dose: A typical dose of Oxytocin for men is 10-20 IU per injection. Men may use Oxytocin for improving social interaction, emotional well-being, and reducing stress.
- For Muscle Recovery: Oxytocin is sometimes used in athletes for its potential to enhance recovery and tissue healing post-exercise. A dose of 10-20 IU per day is typically used during recovery periods, although more research is needed in this area.
- Women (Labor Induction, Lactation, Emotional Health):
- Labor Induction: In clinical settings, the dose for labor induction is highly variable and is typically managed under a healthcare provider’s supervision. It may start at 0.5-1 IU per minute and increase until desired uterine contractions are achieved.
- Postpartum Use: After childbirth, Oxytocin is administered to facilitate uterine contractions and reduce the risk of postpartum hemorrhage. Dosing may range from 10-20 IU based on the needs of the patient.
- Social and Emotional Health: For non-medical use, 10-20 IU may be used to improve bonding, trust, and emotional well-being.
Side Effects:
- Injection Site Reactions: Mild irritation or redness at the injection site is possible, especially if the injection technique is not sterile.
- Excessive Contractions: In clinical settings, excessive Oxytocin administration can lead to overly strong uterine contractions, which may result in complications during labor, including uterine rupture or fetal distress.
- Low Blood Pressure: Some individuals may experience hypotension (low blood pressure) after Oxytocin administration, especially at high doses.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some users may experience nausea or vomiting, particularly when taking higher doses of Oxytocin.
- Headache: A mild headache can occur with Oxytocin use, especially if administered in high doses.
- Water Retention: Oxytocin can cause fluid retention, which may lead to mild swelling in some individuals.
- Overstimulation of Milk Production: In some cases, Oxytocin may lead to excessive milk production or ejection in lactating women.
Cycle Length:
- Short-Term Use: Oxytocin is typically used as needed, particularly for labor induction or postpartum recovery. For non-medical use, cycles can range from a few days to a few weeks, depending on goals (such as improving social bonding or emotional well-being).
- Recovery Use: In cases of muscle recovery or improving mood, Oxytocin can be used for short bursts of 5-7 days to stimulate positive effects, followed by breaks to avoid overstimulation or desensitization.
Post Cycle Therapy (PCT):
- No PCT Needed: Since Oxytocin is a natural hormone, there is no need for post-cycle therapy (PCT). However, for emotional or mental well-being, it may be important to maintain healthy lifestyle practices (e.g., exercise, nutrition) to support emotional balance after Oxytocin use.
Stacking:
- With Other Peptides: Oxytocin is sometimes stacked with growth hormone peptides like CJC-1295 or Ipamorelin to promote muscle recovery and tissue healing after intense workouts.
- With Other Mood Enhancers: For those interested in emotional or social benefits, Oxytocin can be stacked with other compounds like Selank, which may further enhance mood and reduce anxiety.
Important Considerations:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Always consult with a healthcare provider before beginning Oxytocin therapy, particularly if you are pregnant or have any medical conditions.
- Sterile Injection Technique: Use proper sterile techniques when preparing and administering Oxytocin to avoid infections or complications.
- Use in Moderation: While Oxytocin can be beneficial for emotional health and recovery, it is important to avoid excessive use, especially in clinical settings, where overdose can lead to complications such as uterine hyperstimulation.
Related products
Beligas
Beligas